关于 Intel Pentium 4
2000 年 6 月,英特尔发布了迄今为止最新和最强大的处理器。这些基于全新开发的英特尔“NetBurst”微架构。新一代处理器最初使用其 4200 万个晶体管处理数据,除了之前使用的 MMX 和 SSE 命令外,还有 144 个新的 SSE2 命令,并使用四倍并发总线接口交换数据。
新的 NetBurst 微架构中实现了以下功能:
- 超流水线技术:流水线深度是 PIII 的两倍,达到 20 级,在被核心微架构取代之前甚至扩展到 31 级。与 P6 之前的微架构相比,这种相对较长的流水线能够实现更高的时钟速率。
- 快速执行引擎:处理器的算术逻辑单元以处理器内核的两倍频率运行。这将在半条内执行某些命令。这会在执行命令时显着提高数据吞吐量并减少等待时间
- 高性能、四倍并发总线接口:拆分事务深度流水线总线可以同时处理多个请求,而无需在处理器端等待时间
- 高级执行跟踪缓存:是一种高级 L1 指令缓存,用于缓存解密的指令。该技术可实现显着更高性能的指令缓存和更有效地使用缓存内存
- 超线程技术:超线程以两种方式为用户提供增强的性能。通过使用“多线程”软件或在多任务环境中使用软件,例如 Linux 或 Windows XP。当软件被编写为由多个线程(程序部分)组成时,采用 HT 技术的 P4 处理器提供两个逻辑处理器。然后同时处理两个线程。
Introduction
Intel Pentium 4 is a family of high-performance microprocessors that succeeded Pentium III family. Pentium 4 CPUs are based on new NetBurst micro-architecture, which differed significantly from P6 micro-architecture used in Pentium II/Pentium III microprocessors. As an overall CPU performance is proportional to its frequency and its efficiency, to achieve better performance levels many micro-architectures, including P6, strike a delicate balance between faster CPU frequencies and improved efficiency. The NetBurst microarchitecture used different approach - it attempted to improve performance primarily by increasing CPU frequency, often at at the expense of efficiency. One of key elements in this approach was “Hyper-Pipelined Technology” - 20-stage pipeline (not counting decoder stages), that was significantly longer than in previous generation of Pentium processors. While longer pipelines are less efficient than shorter ones, they allow CPU core to reach higher frequencies, and thus increase CPU performance. To improve efficiency of very deep pipeline the Pentium 4 processors included new features: Trace Execution Cache, Enhanced Branch prediction, and Quad Data Rate bus. Intel Pentium 4 CPUs also included 144 new SIMD instructions called SSE2. Because the first generation of Pentium 4 processors, based on Willamette core, proved to be performing not significantly faster, and sometimes slower than the fastest Pentium III microprocessors, Intel added more efficiency improvements to subsequent Pentium 4 core generations - larger size of level 2 cache, faster FSB frequency, SSE3 instruction set, and Hyper-Threading technology. Other features, that were eventually added to the family, are 64-bit instruction set, and Virtualization technology. First Pentium 4 microprocessors, based on Willamette and Northwood cores, as well as some Prescott processors, were referenced by their speed. To differentiate between Pentium 4 CPUs running at the same frequency, but having different features, Intel used one letter suffix, appended to CPU frequency:
- A - Northwood microprocessors with 512 KB L2 cache (for frequencies 2 GHz and lower), or Prescott CPUs with 1 MB L2 cache (for frequencies higher than 2 GHz).
- B - processors with 533 MHz FSB frequency.
- C - processors featuring Hyper-Threading technology and 800 MHz FSB.
- E - Prescott CPUs with 1 MB L2 cache.
Later generations of Pentium 4 CPUs, starting from Prescott core, were assigned processor numbers that uniquely identified processor frequency and features. Please see Intel desktop processor numbers page for more information.
“Pentium 4” brand was used only for high-performance single-core desktop and mobile microprocessors. Server-class CPUs, that were built on NetBurst microarchitecture, were branded Xeon and Xeon MP. Low-cost NeBurst microprocessors were manufactured under “Celeron” brand. Dual-core NetBurst-based microprocessors were branded Pentium D.
All Pentium 4s were manufactured in three types of packages - 423-pin PGA package for socket 423 motherboards, 478-pin micro-PGA package that worked in socket 478 motherboards, and pin-less 775-land LGA package that required socket 775 motherboards. Socket 478 package was used by both desktop and mobile microprocessors, while two other packages were designed for desktop systems only.
我的收藏
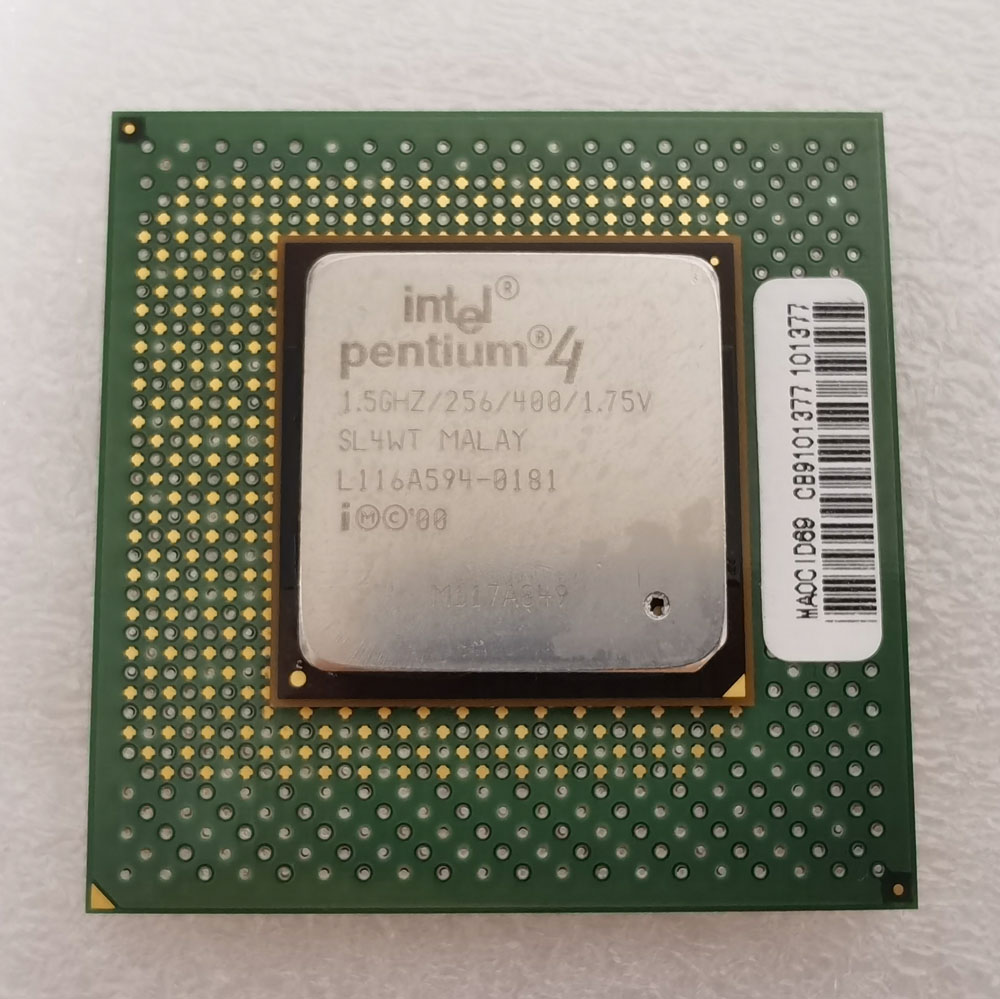
Intel Pentium 4 1.5GHz/256/400/1.75V
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| CPU 类型 | 423-Pin OLGA |
| 核心 | Willamette |
| Socket | 423 |
| 主频 | 1500 MHz |
| 外频 | 100 MHz |
| 总线频率 | 400 MHz |
| 倍频 | x 15 |
| 一级缓存 | 8 KB |
| 二级缓存 | 256 KB |
| 晶体管 | 42,000,000 |
| 制造工艺 | 0.18 µm |
| 电压 | 1.75 V |
| 步进 | SL4WT |
| 生产日期 | 16/2001 |

Intel Pentium 4 1.7GHz/256/400/1.75V
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| CPU 类型 | 478-Pin FCPGA2 |
| 核心 | Willamette |
| Socket | 478 |
| 主频 | 1700 MHz |
| 外频 | 100 MHz |
| 总线频率 | 400 MHz |
| 倍频 | x 17 |
| 一级缓存 | 8 KB |
| 二级缓存 | 256 KB |
| 晶体管 | 42,000,000 |
| 制造工艺 | 0.18 µm |
| 电压 | 1.75 V |
| 步进 | SL5TK |
| 生产日期 | 20/2002 |

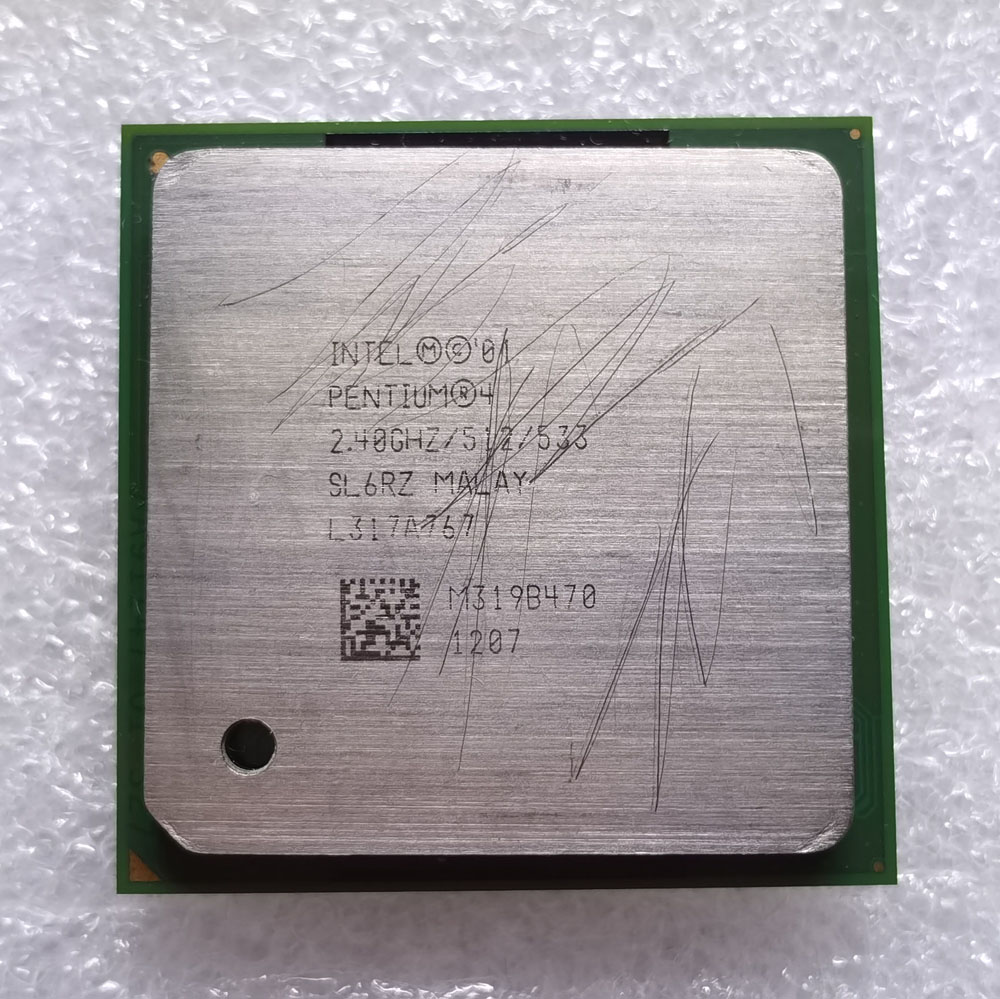
Intel Pentium 4 2.4GHz/512/533
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| CPU 类型 | 478-Pin FCPGA2 |
| 核心 | Northwood |
| Socket | 478 |
| 主频 | 2400 MHz |
| 外频 | 100 MHz |
| 总线频率 | 400 MHz |
| 倍频 | x 24 |
| 一级缓存 | 8 KB |
| 二级缓存 | 512 KB |
| 晶体管 | 55,000,000 |
| 制造工艺 | 0.13 µm |
| 电压 | 1.75 V |
| 步进 | SL6RZ |
| 生产日期 | 17/2003 |